Sersic2D¶
-
class
astropy.modeling.functional_models.Sersic2D(amplitude=1, r_eff=1, n=4, x_0=0, y_0=0, ellip=0, theta=0, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
astropy.modeling.Fittable2DModelTwo dimensional Sersic surface brightness profile.
- Parameters
- amplitudefloat
Surface brightness at r_eff.
- r_efffloat
Effective (half-light) radius
- nfloat
Sersic Index.
- x_0float, optional
x position of the center.
- y_0float, optional
y position of the center.
- ellipfloat, optional
Ellipticity.
- thetafloat, optional
Rotation angle in radians, counterclockwise from the positive x-axis.
- Other Parameters
- fixeda dict, optional
A dictionary
{parameter_name: boolean}of parameters to not be varied during fitting. True means the parameter is held fixed. Alternatively thefixedproperty of a parameter may be used.- tieddict, optional
A dictionary
{parameter_name: callable}of parameters which are linked to some other parameter. The dictionary values are callables providing the linking relationship. Alternatively thetiedproperty of a parameter may be used.- boundsdict, optional
A dictionary
{parameter_name: value}of lower and upper bounds of parameters. Keys are parameter names. Values are a list or a tuple of length 2 giving the desired range for the parameter. Alternatively, theminandmaxproperties of a parameter may be used.- eqconslist, optional
A list of functions of length
nsuch thateqcons[j](x0,*args) == 0.0in a successfully optimized problem.- ineqconslist, optional
A list of functions of length
nsuch thatieqcons[j](x0,*args) >= 0.0is a successfully optimized problem.
See also
Notes
Model formula:
\[I(x,y) = I(r) = I_e\exp\left\{-b_n\left[\left(\frac{r}{r_{e}}\right)^{(1/n)}-1\right]\right\}\]The constant \(b_n\) is defined such that \(r_e\) contains half the total luminosity, and can be solved for numerically.
\[\Gamma(2n) = 2\gamma (2n,b_n)\]References
Examples
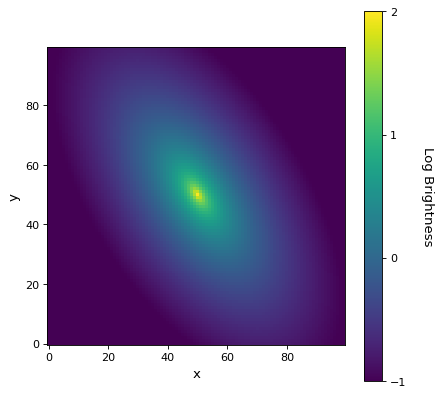
import numpy as np from astropy.modeling.models import Sersic2D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x,y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(100), np.arange(100)) mod = Sersic2D(amplitude = 1, r_eff = 25, n=4, x_0=50, y_0=50, ellip=.5, theta=-1) img = mod(x, y) log_img = np.log10(img) plt.figure() plt.imshow(log_img, origin='lower', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1, vmax=2) plt.xlabel('x') plt.ylabel('y') cbar = plt.colorbar() cbar.set_label('Log Brightness', rotation=270, labelpad=25) cbar.set_ticks([-1, 0, 1, 2], update_ticks=True) plt.show()
Attributes Summary
This property is used to indicate what units or sets of units the evaluate method expects, and returns a dictionary mapping inputs to units (or
Noneif any units are accepted).Methods Summary
evaluate(x, y, amplitude, r_eff, n, x_0, …)Two dimensional Sersic profile function.
Attributes Documentation
-
amplitude= Parameter('amplitude', value=1.0)¶
-
ellip= Parameter('ellip', value=0.0)¶
-
input_units¶ This property is used to indicate what units or sets of units the evaluate method expects, and returns a dictionary mapping inputs to units (or
Noneif any units are accepted).Model sub-classes can also use function annotations in evaluate to indicate valid input units, in which case this property should not be overridden since it will return the input units based on the annotations.
-
n= Parameter('n', value=4.0)¶
-
param_names= ('amplitude', 'r_eff', 'n', 'x_0', 'y_0', 'ellip', 'theta')¶
-
r_eff= Parameter('r_eff', value=1.0)¶
-
theta= Parameter('theta', value=0.0)¶
-
x_0= Parameter('x_0', value=0.0)¶
-
y_0= Parameter('y_0', value=0.0)¶
Methods Documentation